58 Digital Marketing Terms to Know

Familiarizing yourself with digital marketing words and phrases will allow you to confidently speak with your clients, marketing and sales teams, peers, or your marketing agency. This quick guide will define some commonly used digital marketing terms to keep you in the know.
58 Digital Marketing Terms to Know
1. A/B Testing
A/B testing or “split testing” is a marketing technique that compares two versions of a campaign to see which performs better. Marketers "split" an audience into two groups and show version A to one audience and version B to the other. Differences between the two campaigns could be changes to the ad copy, color schemes, or call-to-action. A/B testing allows marketers to know which elements of a social ad, landing page, e-mail subject line, etc. is most effective in bringing in the desired results.
2. Analytics
Analytics data enables marketers to evaluate the performance of marketing initiatives and provides deep insights into consumer behavior. Analytics are used for websites, social media, and email campaigns, and provide data such as time on site, demographics, pages viewed and more.
3. B2B
Business-to-Business (B2B) simply refers to any company focused on selling products or services to other businesses rather than a general consumer - think office supplies, software, specialized products or services, etc. Key players in the field include manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, farms, construction firms, service industries, the government, and non-profit organizations.
4. B2C
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) refers to any company focused on selling products or services directly to consumers. Examples of B2C include individuals shopping at a clothing store, eating at a local restaurant, making a purchase online or subscribing to a streaming service.
5. Backlink
Also known as inbound links, backlinks are outside links that point to your website or web page. Backlinks are used in Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and building these links is an off-page technique to increase the ranking of a website in search engine results.
6. Blogging
A blog is a website or webpage that is regularly updated and can be used for personal or business use. B2B marketers who use blogs receive 97% more links to their websites than those who do not.
7. Bounce Rate
A “bounce” occurs when a website visitor lands on a page, does not interact and quickly leaves the site. The bounce rate compares the amount of single-page visits against the total number of visits. Marketers aim to keep bounce rates low by posting engaging content to keep visitors on the site for longer periods.
8. Buyer Persona
A representation of a business’s ideal buyer, based on market research, real data, demographics, behavior patterns and motivations of existing customers. A detailed buyer persona guides product development helps determine the lead quality and allows a business to attract the most valuable leads.
9. Call-To-Action (CTA)
A CTA refers to specific words or phrases that can be incorporated into sales scripts, advertising messages and web pages. The objective of a CTA is to prompt a desired response from the audience by using phrases such as “call now”, “find out more” or “visit a store today.”
10. Churn Rate
Churn rate is the number of customers who leave a company during a given period. To calculate, simply divide the number of churned customers by the total number of customers.
11. Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
The click-through rate of an ad is the percentage of people who click on the ad after seeing it. To calculate, divide the number of people who click the ad after viewing by the total number of impressions the ad received.
12. Clickbait
Clickbait is a piece of content that aims to increase web traffic by intentionally misrepresenting content in order to pull users onto a website. Clickbait generally captures users with an intriguing headline - such as “this will blow your mind!”, or “you won’t believe this!”- but fails to deliver on the user’s expectations.
13. Content Management System (CMS)
A CMS is a software that facilitates creating, editing, organizing, and publishing digital content. There are many CMS tools available – ranging from free to expensive and simple to robust. One CMS industry leader, HubSpot, allows users to “Create and edit blog posts, landing pages, site pages, and emails with ease… then manage, optimize, and track the performance of your content with the same platform you used to create it.”
14. Conversion Path
Website visitors will visit several pages before making a transaction - purchasing an item, completing a form, downloading an eBook, etc. The conversion path is the order of pages visited, and links clicked by a website visitor which leads to a successful transaction being completed.
15. Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is the percentage of website visitors that complete a desired goal (a conversion) out of the total number of visitors. A high conversion rate indicates successful marketing and streamlined web design.
16. Customer Acquisition Costs
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) represents the resources and costs acquired to gain an additional customer. Customer acquisition cost is an essential business metric that is commonly used in conjunction with the customer lifetime value (LTV) metric to measure the value generated by a new customer.
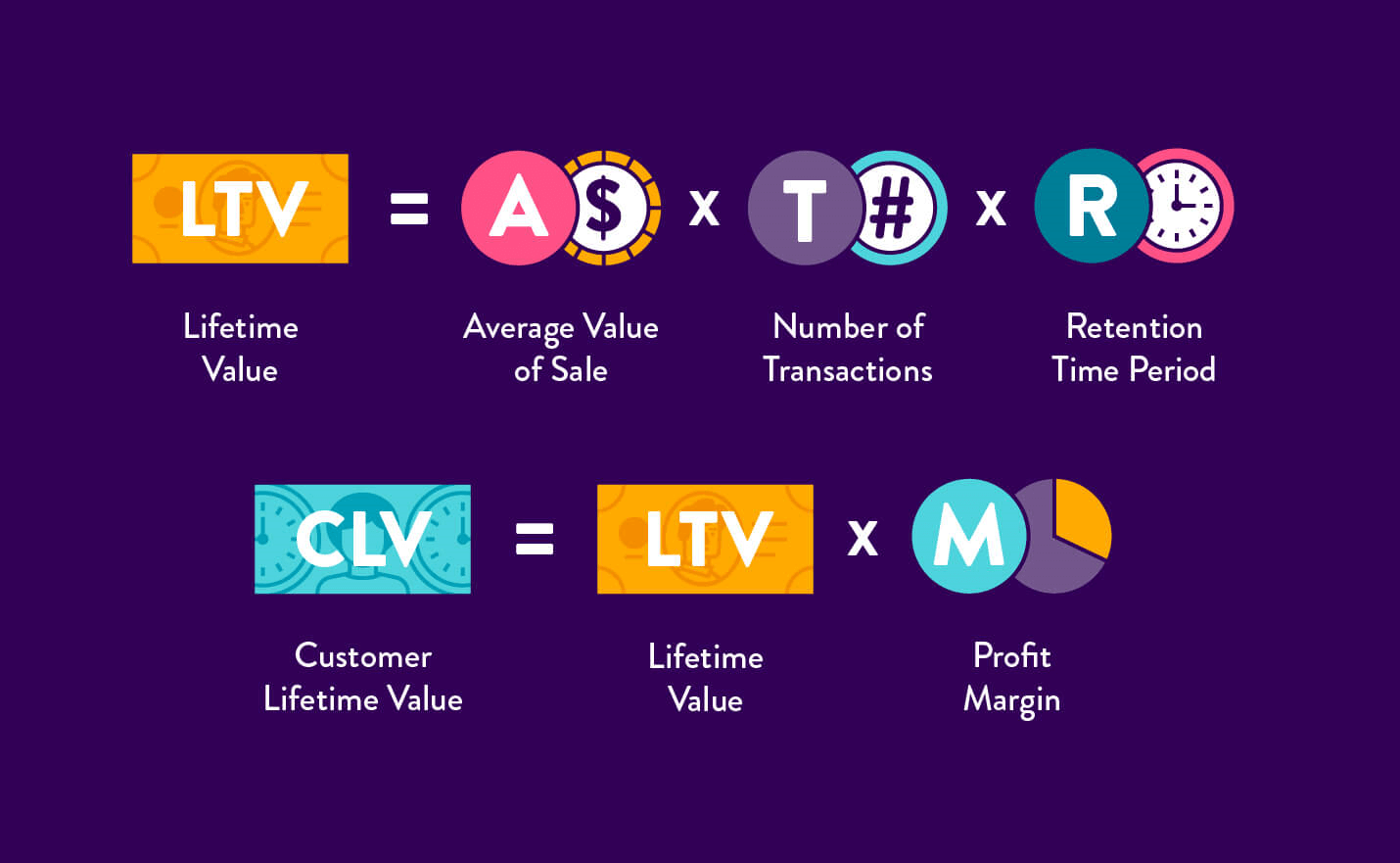
17. Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
The customer lifetime value (LTV) is the total revenue a company anticipates earning over the course of their relationship with a single customer. Customer acquisition costs, operating expenses, and production costs of the goods or services that the company is manufacturing are all accounted for in the customer LTV.
18. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM systems collect customer information from a variety of sources, including email, websites, physical stores, call centers, and mobile sales. CRM systems help provide businesses with an accurate view of their customer base to help them effectively market and sell products and services.
19. Demographics
Demographics are characteristics of a selected population that allows marketers to segment or target a specific audience in marketing and advertising strategies. Commonly-used demographics include age, gender, income, family life, social class, etc.
20. Display Advertising
A staple in digital advertising, display ads are text, image or video ads that are shown on a web page. A form of paid advertisement, these ads are displayed on websites using a set of keywords that are matched to the hosting website’s theme.
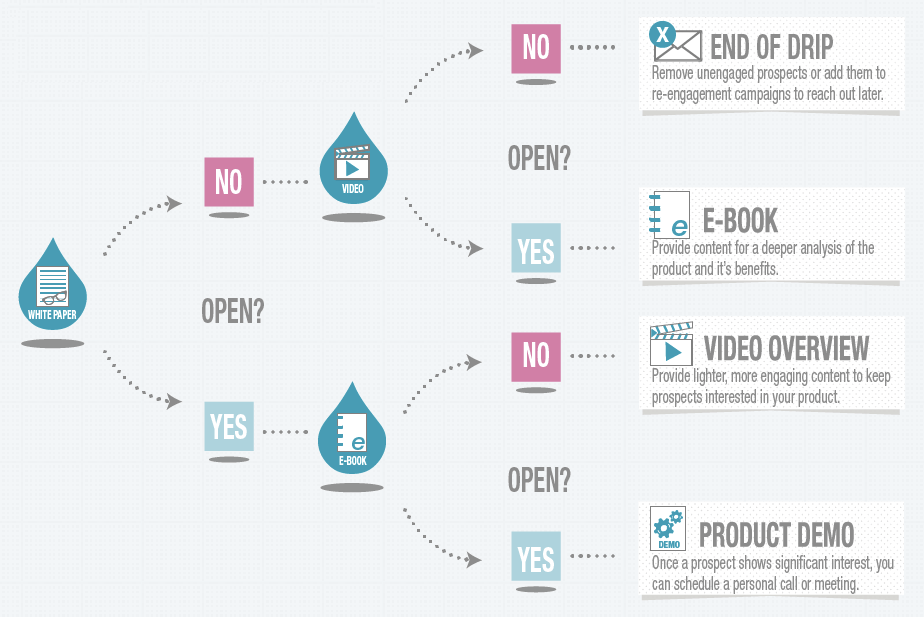
21. Drip Campaign
Drip campaigns are automated emails that are sent based on a specific timeline or user action. These emails enable marketers to stay in touch with groups of people based on events (like when a new user subscribes or how often that user visits a site) and gives people the right information at the right time.
22. Ecommerce
Ecommerce, also known as electronic commerce, involves the buying or selling of goods and services using the internet. Ecommerce marketing aims to drive sales using SEO, social media, paid traffic, remarketing, influencer marketing and other paid and non-paid strategies. Ecommerce is a thriving industry with global retail eCommerce sales projected to reach $27 trillion by 2020.
23. Engagement
“Engagement” is used to describe any kind of interaction a piece of content receives - likes, shares, comments, etc. When a user gives a piece of content attention – a relationship has begun to form between the user and the brand. The engagement rate is a great tool to use when determining the success of a campaign or comparing multiple ads.
24. Email List Segmentation
Email list segmentation is an email marketing technique that segments (or splits) a subscriber list, based on any number of conditions. It is a technique used by marketers to send relevant communications to specific people in an email marketing list.
25. Email Opt-In
Two email marketing signup methods are available – single and double opt-in. Single opt-in occurs when a subscriber signs up for emails via a subscription form and are immediately added to an email list. When a subscriber signs-up via a subscription form and then receives a confirmation email to authorize they want to receive emails, this is known as double opt-in.
26. Evergreen Content
Evergreen content is content that remains appropriate to the reader long past its publication. This type of content is timeless, offers the highest-quality information and offers huge SEO benefits. Examples include lists, tips, “How To” tutorials and product reviews.
27. Geotarget
Geotargeting is simply targeting an audience based upon their location. This can be performed using numerous identifiers including country, state, city, zip code or IP address. Geotargeting is often used for local advertising.
28. Hashtag
Using the “#” symbol before a relevant keyword or phrase (no spaces) on social media sites like Instagram and Twitter, helps categorize posts and allows them to show up more easily in search.
29. Impression
An impression occurs when an ad, content or post is loaded and displayed. The term is synonymous with “view” – page views, ad views or post views.
30. Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing is a method for attracting customers to a brand via content marketing, social media marketing and SEO. This term was first coined by HubSpot co-founder Brian Halligan. Today, HubSpot defines inbound marketing as:
“a business methodology that attracts customers by creating valuable content and experiences tailored to them. While outbound marketing interrupts your audience with content they don’t want, inbound marketing forms connections they’re looking for and solves problems they already have.”
31. Indexing
Indexing is the process search engines use to organize information before a search to enable lightning-fast responses to queries. Search engine indexing processes everything which is found on a webpage, including keywords, images, headings, links etc.
32. Influencer Marketing
Individuals who have the power to shape the purchase decisions of others because of their authority, position, or knowledge are known as “influencers.” Some brands use influencer marketing by collaborating with celebrities, industry experts, thought leaders, journalists, and athletes, on social media and ad campaigns. The goal of influencer marketing is for the influencer to set the trend and encourage their followers to buy the products and services they promote.
33. Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
KPIs (key performance indicators) are benchmarks used to track the progress marketers make while working towards their goals. KPIs are straightforward metrics marketers aim to hit to assure the project or department is on track and growing.
34. Keyword
Words and phrases commonly used by search engines to discover online content are called “keywords.” Digital advertising and website search engine placement can be optimized to match high traffic keywords, making it more likely that web searchers will end up on a certain site. Keyword research is a powerful and necessary internet marketing tool.
35. Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is an unethical SEO technique that loads a page with keywords to manipulate and influence search engine results. According to Google, “Filling pages with keywords or numbers results in negative user experience and can harm your site's ranking.”
36. Landing Page
After a user clicks on a display or paid search ad, they are directed to a designated web page or landing page.
37. Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)
LSI is a search engine indexing method that creates a relationship between keywords and phrases to help understand the subject matter of a text. LSI allows search engines to display more accurate search results.
38. Lead
A lead is a prospective customer who communicates with a business via call, email, or online form, with intent to purchase. Businesses attract leads through a variety of methods, including advertising, paid traffic, trade shows, direct mailings, third parties, and more. Once a company has secured a lead, they can connect with the potential customer to determine their intent and interest.
39. Lookalike Audience
Lookalike audiences target people who are similar to a business’s existing customer base. Lookalike audiences help improve conversion rates when running online display, Facebook, mobile display or any other kind of digital marketing campaign.
40. Off-Page Optimization
Off-page optimization is an SEO technique that involves all external website processes that can affect search engine reach and rankings. Examples include creating links on third party sites, building links on established/globally recognized sites, link building on related websites, establishing links on social media networks and submitting the website to search engines and web directories.
41. On-Page Optimization
A component of SEO, on-page optimization refers to factors that influence a web site or web page listing in organic search results. These factors are controlled by the marketer or by coding on the webpage. Examples of on-page optimization include HTML code, meta tags, keyword placement, and keyword density.
42. Organic Search
Unpaid search results are considered organic. The opposite of paid search results (pay-per-click advertising), organic search results are constructed on relevance to the user's search query, domain authority, links, and other organic ranking factors.
43. Organic Traffic
In contrast to paid traffic, which defines site visits generated by paid ads, traffic is deemed “organic” when visitors use a search engine and are not “referred” by any other website.
44. Pay-Per-Click (PPC)
A driver of paid traffic in which advertisers are only charged for their ad once it is clicked. PPC ads are associated with social media, and search engine advertising – search advertising, remarketing, display advertising, shopping ads and video ads. WordStream considers PPC advertising to be “a way of buying visits to your site, rather than attempting to “earn” those visits organically.”
45. Personalization
Advertising personalization uses customer insights to increase an ad’s relevancy. These data points can be simple insights (such as basic demographic information; or more specific like a niche interest, buying intent and behavioral patterns). Personalization makes a consumer feel that the brand is speaking directly to them and addresses their specific needs.
46. Paid Traffic
Paid traffic is any website viewer that visits a site after seeing a paid advertisement. Paid ads consist of banners, advertisements, pop-ups, and videos. A common form of paid traffic is Pay Per Click (PPC) advertising. Some advantages of paid traffic include fast set-up, quick results in the form of more leads, and increased exposure for your brand.
47. Rankings
A site’s “ranking” is where the website appears in search engine results. The ranking may shift up or down over time for different search terms. The ranking is specific to each keyword, meaning a website may have keywords that rank on the first page and others that do not.
48. Referral
When users click on a link that sends them to another, external webpage, they are said to have been “referred” there. A referral is a website visit that came from another website as opposed to coming from a Google search, for example.
49. Responsive Design
A website that changes based on the device the consumer uses is considered “responsive”. Mobile, laptop and desktop devices offer different views of a website, and a “responsive design” accommodates each view. Responsive, mobile-friendly websites are prioritized to show up in Google searches on mobile devices. In 2018, 58% of website visits were from mobile devices, and these devices made up 42% of total time spent online.
50. Retargeting/Remarketing
Retargeting, also known as remarketing, is serving ads to visitors who have previously viewed a website. Picture this: Your business sells shoes online. A visitor scans your website but does not make a purchase. You can “retarget” the user after a set amount of time by serving social media ads, display ads, etc. to further promote your products and encourage the website visitor to make a purchase.
51. Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI is a way to measure the profitability of marketing investment. If the ROI on investment is negative, it generally means the business is losing money on that endeavor. Simple ROI Formula: (Sales Growth - Marketing Cost) / Marketing Cost = ROI
52. RSS feed
RSS = Really Simple Syndication. Instead of manually checking individual websites (news sites, blogs, and more) users can keep track of updates to multiple websites in one place using an RSS feed.
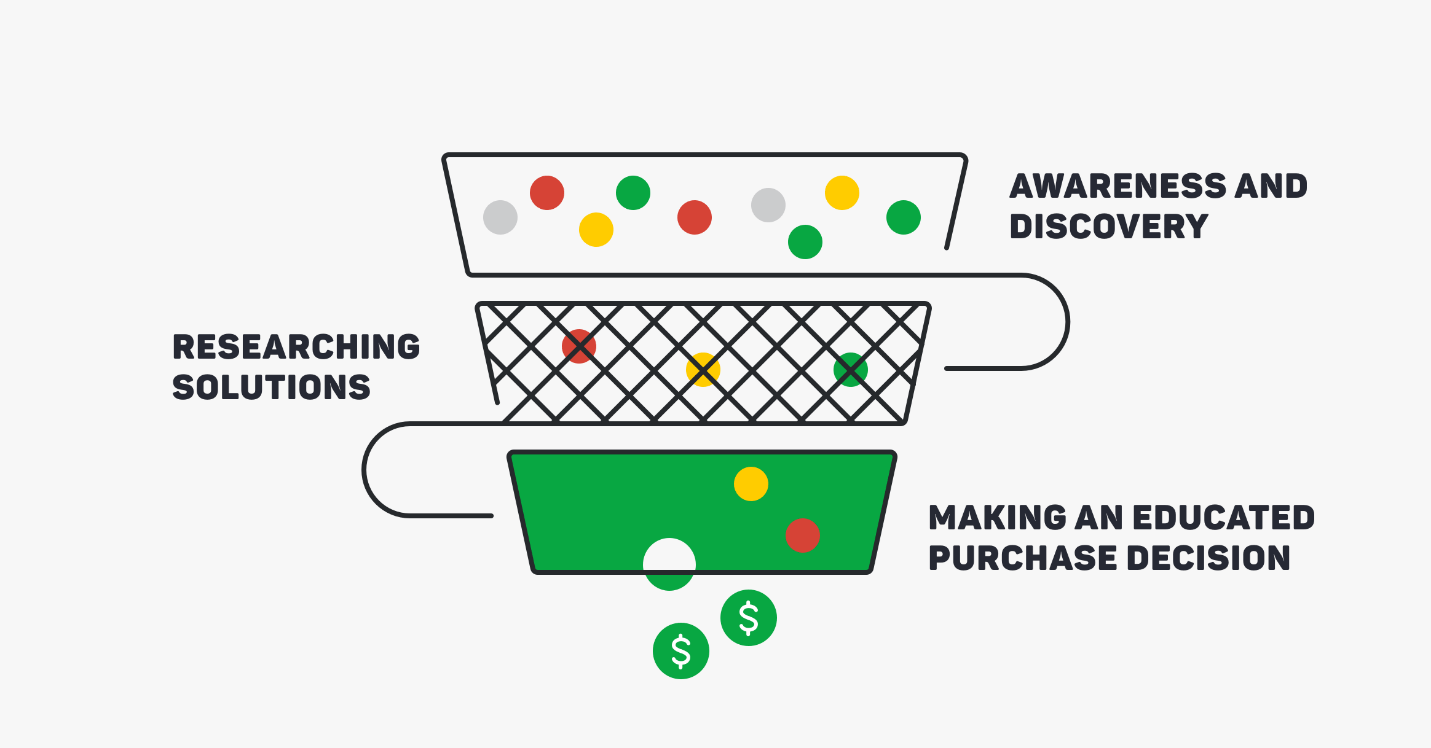
53. Sales Funnel
A sales funnel is an illustration of the prospect’s journey from the first contact with a business until a completed purchase.
54. SEO
SEO improves a website’s performance and positioning in organic search engine results using a variety of techniques. SEO focuses on improving rankings by using on-page and off-page optimization. A common SEO strategy should include content creation or improvement, optimizing for keywords, ensuring on-page SEO is set up correctly (title tags, meta descriptions, headers, etc.) technical and code improvement, and link building.
View a collection of helpful SEO infographics and stats here.
55. Social Listening
Social listening refers to analyzing the conversations and trends happening around a particular brand or industry on social media and using those insights to shape future marketing decisions. Listening to what customers are talking about online can influence business operations, advertising campaigns, product updates, and more.
56. Spam
The term "spam" is internet slang that refers to unsolicited commercial emails or advertisements. For example, some tell-tale signs that your marketing emails may be marked as spam include sending emails to purchased lists or contact’s whom you do not have permission to email. Learn the defining characteristics of a legitimate email marketing campaign here.
57. UI
User Interface (UI) is the area with which a user interacts with a website or app through a digital device. Good UI is fluid and easy for most people to understand and navigate.
58. UX
User Experience (UX) is how users interact with an app or website (where they click, which pages they visit). UX can be manipulated by testing different page layouts, CTAs, colors, content, etc. to improve conversion rates.